Page 143 - FIGHT AGAINST UNCERTAINTY 5 FEB 2021
P. 143
The Imperial College Non- A
Pharmaceutical Intervention
Impact Model
The Imperial College model uses a Bayesian
hierarchical approach aggregating data
from multiple countries or regions and
uses an estimated distribution for the serial
interval, the time from infection to onset of
symptoms and the time from onset to death.
Findings:
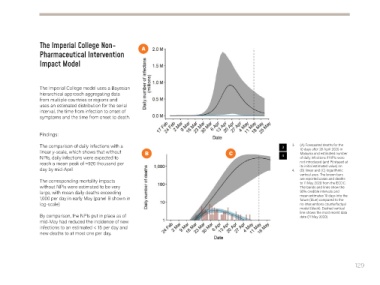
The comparison of daily infections with a 3 3. (A) Forecasted deaths for the
linear y-scale, which shows that without B C 10 days after 26 April 2020 in
Malaysia and estimated number
NPIs, daily infections were expected to 4 of daily infections if NPIs were
reach a mean peak of ~920 thousand per not introduced (and Rt stayed at
its initial estimated value) on
day by mid-April 4. (B) linear and (C) logarithmic
vertical axes. The brown bars
The corresponding mortality impacts are reported cases and deaths
to 11 May 2020 from the ECDC.
without NPIs were estimated to be very The bands and lines show the
large, with mean daily deaths exceeding 95% credible intervals and
1,000 per day in early May (panel B shown in mean estimates 10 days into the
future (blue) compared to the
log-scale) no interventions counterfactual
model (black). Dashed vertical
line shows the most recent data
By comparison, the NPIs put in place as of date (11 May 2020).
mid-May had reduced the incidence of new
infections to an estimated < 15 per day and
new deaths to at most one per day.
129